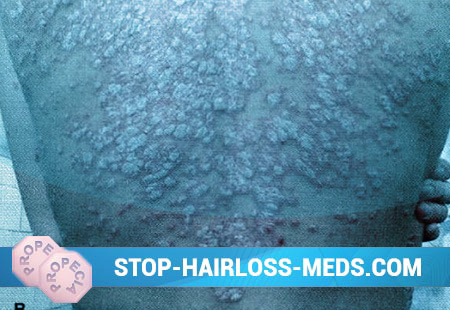
There are more than 20 different schemes and techniques that have a positive effect in psoriasis, but none of them allowed for a complete cure of dermatosis. The lack of a unified concept of the etiopathogenesis of psoriasis, data on the multifactorial nature of dermatosis cause a variety of drugs and methods for treating the disease in patients. In the recent past, the treatment of patients with this dermatosis was rather symptomatic in nature; at present, it is safe to say about evidence-based pathogenetic therapy for psoriasis. General and external treatment is performed taking into account the stage of the process, seasonality, clinical type of the disease.
In the past, various means were used to treat psoriasis: injections of milk, sulfur, oxygen injections, cystine, D-lactic acid solution, antipsoriatikum preparations, psoriasin preparations, glycerin extracts from psoriatic scales and plaques, specific vaccine, Fowler fluid. In addition, X-ray irradiation of the thyroid and helical glands, indirect radiotherapy were used. However, none of the above methods have found any use for themselves due to lack of effectiveness or high frequency of side effects. The general treatment of patients with advanced psoriasis in the progression stage has long been proposed to be carried out with calcium preparations that provide anti-inflammatory, hyposensitizing and membrane stabilizing effects.
Preparations of sodium, potassium, and magnesium — potassium chloride, sodium thiosulfate, and also potassium asparaginate — have a stimulating effect on the adrenal cortex and normalize tissue metabolism. Sodium thiosulfate also has a pronounced anti-inflammatory, detoxifying and hyposensitizing effect, stimulates the function of the adrenal cortex.
Calcium preparations normalize adenylate cyclase activity, decrease capillary permeability. Of calcium salts, gluco-nat, glycerophosphate, chloride, pantothenate, lactate are used. In the treatment of patients with psoriasis, magnesium sulfate has not lost its relevance, the presence of a sulfur atom in which affects the normalization of the mitotic activity of keratinocytes of the epidermis, the stimulation of the adenylate cyclase system with activation of cAMP. Etiotropic treatment is currently not developed. The focus is on pathogenetic and symptomatic effects. For exudative rashes, common rashes up to erythroderma, acute and severe process with signs of intoxication, accompanied by intense itching, use detoxification means and methods. In a progressive stage, a 25% solution of magnesium sulfate is administered intravenously or intramuscularly (10-12 injections), a 30% solution of sodium thiosulfate intravenously in the amount of 10-15 injections, antihistamines (suprastin, pipolfen, tavegil, etc.) inside or parenteral, intravenous drip hemodez 200-400 ml every other day or 2 times a week.
Hemodez is a drug that contains a 6% aqueous solution of vinylpyrolidone and ions of magnesium, sodium, potassium and chlorine. The drug has dehydrating properties, can bind and excrete toxins with urine, normalize the level of free fatty acids in the blood, positively affect the blood coagulation system and fibrinolysis. Other plasma-substituting solutions can be used (polyglukin, reopolyglukine, etc.), but they are somewhat weaker. Vitamin preparations and their biotransformation products – coenzymes – are widely used in the treatment of psoriasis. The mechanisms of their action are very diverse.
In psoriasis, thiamine (vitamin B1), pyridoxine (vitamin B6), riboflavin (vitamin B2), cyanocobalamin (vitamin B12), folic acid, tocopherol acetate (vitamin E), retinol (vitamin A) have found their use.
The undoubted advantage of using vitamins and coenzymes is the absence of serious side effects and complications, with the exception of individual intolerance. The purpose of therapeutic measures at the beginning of the disease is to stop the progression of the process. It is formed by the general methods of treatment: the appointment of vitamins and calcium preparations. The following treatment regimen proved itself, especially with exudative psoriasis: intravenous administration of 10% solution of calcium chloride or gluconate 10 ml every other day and intramuscular injections of vitamin B12 (400 μg) every other day, ingestion of folic and ascorbic acids. The duration of such treatment is 1-3 months. At present, promising detoxification methods such as hemodialysis, hemosorption, plasmapheresis, hemofiltration, which are especially needed during the progressive process, have been developed and are being introduced. In patients with psoriasis, especially severe forms, there is congestion with pathological immune circulating complexes, depression, blocking of the physiological systems of defense and regulation, functional disorders of the gastrointestinal system. This situation forms the syndrome of endogenous intoxication, as a result of which an excess amount of intermediate and final metabolites accumulate in the body, having a toxic effect on the functional state of the most important organs.
The use of efferent methods has a detoxifying systemic effect, in which, as a result of the removal of xenobiotics and various toxic effects, non-drug stimulation of the systems of natural immunity, physiological mechanisms of sanogenesis with the normalization of life processes is carried out. Detoxifying hemosorption has been used for many years to treat all forms of psoriasis. Its high efficacy in patients with severe and common forms of the disease has been established. Hemosorption can be used in combination with traditional methods of treatment. Also according to the principle of effective exposure, plasmapheresis is also used, which has a pronounced therapeutic effect. Funds that correct microcirculation disorders, stabilize the microcirculatory vessels, have a beneficial effect on the cyclic nucleotide system, restore cell membranes, and have a hypoglycemic and hypocholesterolemic effect. In psoriasis, andecalin, doxyium, pentoxy-filin (trental), parmidine, complamine, cavinton are used. Heparin in psoriasis is used to prevent the alteration of keratinocyte β-adrenergic receptor immune complexes, inhibit thrombogenesis and stimulate plasmin formation, and restore microcirculatory disorders. Heparin is advisable to use in common forms of psoriasis vulgaris, psoriatic arthritis and erit-rodermia. The beneficial effect on the course of psoriasis in patients is found by Essentiale — a preparation containing “essential” (necessary) phospholipids — diglycerol esters of choline phosphoric acid and unsaturated fatty acids — linoleic (up to 70%), linolenic and others. Zixorin induces the oxidase activity of microsomal liver enzymes, increases the formation of glucuronides, promotes the excretion of endogenous and exogenous metabolites, which generally has a positive effect on the course of the psoriatic process. By biostimulants, traditionally used to treat patients with psoriasis, include pyrogenal and prodigiozan. An important property of Prodigiosan, in addition to the action on T-lymphocytes, macrophages, is the stimulation of the synthesis and emission of corticosteroid hormones, interferons, activation of the pituitary-adrenal system. Levamisole is able to restore the altered functions of T-and B-lymphocytes and phagocytes, to stimulate neutrophil chemotaxis. Due to its thymomimetic effect, the drug can increase the reactivity of immune cells to thymic hormones.
Levamisole does not affect the normal immune response, but restores the latter when it is deficient, and can reduce the CIC content in the blood. There is evidence of the promise of using tactivin as part of immunocorrective therapy for patients with psoriasis. The drug stimulates the quantitative and functional indicators of the T-cell system, normalizes the production of lymphokines, including interferons.
Timalin also performed well in treating patients with psoriasis. The drug regulates the number of T-and B-lymphocytes, has a positive effect on phagocytosis, there are processes of stimulation, regeneration and blood formation. Imunofan has the ability to possess immunoregulatory, hepatoprotective, detoxifying action. Immunoregulatory action of imunofan is manifested by the restoration of impaired cellular and humoral immunity parameters. Proved the effectiveness of imunofana with the most diverse pathology, including psoriasis. In the stationary period of psoriasis, pyrotherapy using intramuscular injections of pyrogenal or prodigiosan is recommended. If treatment with these agents is ineffective, cytostatics from the group of antimetabolites, in particular, methotrexate can be used. The drug is used one tablet 2 times a day in courses for 5-7 days with weekly breaks. Fewer complications occur when taking methotrexate once a week during the day: 2 tablets every 12 hours.
Indications for the use of systemic suppressive drug therapy drugs are psoriatic erythroderma, pustular form of psoriasis and polyarthritis, as well as common vulgar psoriasis resistant to other treatments. The drugs of this group include: neotigazon, aromatic retinoids – etretinat (tigazon), isotretinoin (roaccutane), soriaten. Recently, much attention has also been paid to the use of vitamin D3 and its analogues, takalcitol and calcipotriol, for psoriasis. Interacting with specific receptors in keratinocytes, calcipotriol can cause a dose-dependent inhibition of proliferation of these skin cells, accelerating their morphological differentiation.
Vitamin D3 analogs are widely used in psoriasis; they are well tolerated and are a worthy alternative to topical corticosteroids. Topical cortico-steroids in combination with dithranol, calcipotriol, pimecrolimus and tacrolimus, as well as derivatives of zinc pyrithione (skincap) and tar preparations are currently used as external therapy for psoriasis. External treatment depends on the stage of the disease. In the progressive period, only lubrication of the affected skin is applied with a weak peeling (1-2% salicylic) or corticosteroid ointment. In case of a pronounced inflammatory phenomenon, you can add ointments and creams with glucocorticoid hormones. In the stationary and regressive periods, 3-5% white or 2% yellow mercury, 5-10% ichthyol ointment is used. For the scalp, you can use a 2% mercury-salicylic ointment.
It is advisable external use of DMSO (dimethyl sulfoxide). Applied to the foci of psoriatic elements or to the affected joints in the form of creams or ointments (5-10% or 20%), the drug penetrates deep into the epidermis, dermis, into the synovial membranes of the joints, has an anesthetic, anti-inflammatory and bactericidal effect in the joints, periarticular tissues, as well as directly in the skin. A pronounced effect appears after the use of drugs in the tar in increasing concentrations (5-10-20%). First use tar paste, then ointment. To enhance the effect of the latter, they gradually change the method of their application: lubrication, application under the dressing, then under the compression dressing, rubbing. The tar bath is an excellent effect – a general warm bath for 30-60 minutes, which is taken 10-15 minutes after rubbing pure tar into the affected skin. In case of surface infiltration of psoriatic elements, they are lubricated with heparin ointment with the addition of 50-70% dimexid solution, furoccin, a mixture of tar, ether and alcohol, taken in equal proportions, with a 5% potassium permanganate solution, and Castellani liquid. In the case of psoriatic erythroderma, it is necessary to use glucocorticosteroids. Psoriatic arthritis requires combined treatment with corticosteroids, methotrexate, anabolic drugs and indomethacin (brufen); In addition, they use mud therapy, paraffin baths, massage, therapeutic exercises, and ultrasound. It should be noted that the treatment of patients with psoriasis for any concomitant disease with streptomycin or penicillins often leads to exacerbation of the course of psoriasis, and especially psoriatic arthritis.
It is necessary to limit carbohydrates in food, to use unloading diets, including fasting, general heat (36-37 ° C) baths every other day, appropriate psychotropic drugs, removal (according to indications) of the tonsils. Physiotherapy treatments for psoriasis are currently complemented by PUVA therapy or photochemotherapy. This treatment has a cytostatic effect: irradiation of the skin with long-wave ultraviolet rays (UVA) of high energy, carried out after ingestion of photosensitizing drugs – puvalene, psoralen, etc. -4 times a week (20-40 procedures). Side effects and complications of PUVA therapy are a tendency to the appearance of tumor and precancerous conditions, radiation damage to the eyes, the formation of photodermatosis, cataracts, toxic hepatitis, dry skin, papillomatosis, dizziness, dyspeptic disorders, itching.
For patients with the winter form of psoriasis, a combination of this treatment with general ultraviolet irradiation is useful, starting with sub-erythemal doses. On torpid current plaques it is necessary to apply erythemic doses of ultraviolet rays. You need to know that ultraviolet radiation can not be combined with the reception of methotrexate. From other physiotherapeutic methods of treating psoriasis, phonophoresis of ointment with hydrocortisone, laser therapy in combination with a permanent magnetic field (magnetic laser therapy) are used. Also use induction therapy, laser puncture, acupuncture, hyperthermia in a heat chamber (42-45 ° C). Applications of ozokerite, paraffin can be used both for the treatment and for the prevention of relapses. For the prevention of recurrence of psoriasis, ultraviolet irradiation of the entire skin is recommended during remissions.
The problem of treating patients with psoriasis remains highly relevant in modern conditions, despite the large arsenal of proposed drugs and developed therapies. A significant part of the proposed therapeutic agents is not sufficiently effective, since it does not take into account the nature and severity of immunological and metabolic shifts in the body of patients, and also has a diverse range of side effects.
It is necessary to further develop pathogenetically substantiated areas of therapy that effectively correct immunological and metabolic disorders in the body in case of psoriasis, reduce endotoxicosis and shorten the duration of treatment for patients. During the stabilization process, sanatorium-resort treatment is recommended. Also, patients with psoriasis in the inpatient and regressive periods recommended spa treatment: heliotherapy, sea bathing, sulfur baths, massage, exercise therapy. With summer form of psoriasis, heliotherapy is absolutely contraindicated. In all periods of psoriasis, it is necessary to observe a rational sanitary and hygienic regimen, diet therapy.
