What is Amyloidosis of the Skin?
Amyloidosis is a heterogeneous disorder of protein metabolism, in which the glycoprotein amyloid is deposited extracellularly in the tissues of various organs. There are systemic and local amyloidosis. In the latter, amyloid deposits are localized only in a specific organ.
Causes of Amyloidosis
It is believed that the disease is caused by a violation of the transformation of proteins in the body of the patient. As a result, in the body in various organs and tissues deposited pathological protein – amyloid.
Symptoms of Amyloidosis of the Skin
Currently, there is a gradation, according to which the disease is divided into 3 types:
- primary systemic amyloidosis;
- local lichenoid amyloidosis;
- secondary system amyloidosis.
The primary systemic type of the disease is quite rare among the population. Most often develops in older people. The protein amyloid in large quantities at the same time accumulates in the stomach and intestines, in the lumen of blood vessels, in skeletal muscles, and also in the skin. As a result of such metabolic disorders characteristic external changes occur. The patient’s tongue may significantly increase in size, sometimes even 3-4 times, it becomes more dense, it may not even fit in the oral cavity, its mobility is impaired. The skin of the face becomes pale in color. In the area of the natural folds of the skin (most often in the groin, in the area of the pubis, thighs, armpits, etc.) very small nodules appear, the skin over which is pale. They tend to group together and merge. As a result of the latter, large pathological foci are formed on the skin, which have a darker compared to healthy skin color and a rough surface. There are violations in the general condition of the patient. He constantly experiences weakness, pain in skeletal muscles, disrupted mobility of joints. As a rule, itching is not observed. In some cases, patients simultaneously with skin amyloidosis have comorbidities, most often in the form of myeloma (tumors of the nerve trunks) and the appearance of proteins in the urine, which indicates a violation of protein metabolism in the patient’s body.
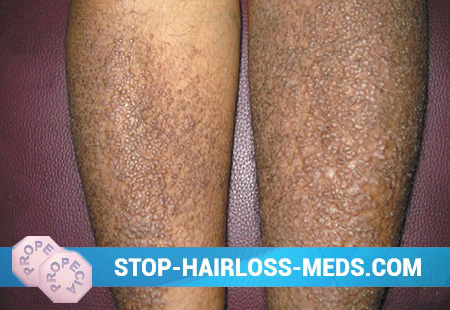
Primary localized form of amyloidosis. This type of disease is also called lichenoid. Multiple nodules appear on the patient’s skin, having a brownish color and closely grouped with each other. Sometimes on the surface of the skin above the nodules abundant peeling is defined. They are conical or flat in shape. Although the nodules are prone to grouping, they still under no circumstances merge with each other. The external signs of this type of disease in many cases resemble atopic dermatitis. Sometimes it looks like lichen planus. During the illness, the patient complains of the sensation of severe itching in the area of pathological foci. In the region of the pathological foci, warty-like growths may appear. The most frequent locations of pathological foci in a lichenoid form of amyloidosis are the region of the legs, thighs, and much less often the face.
Secondary systemic amyloidosis. As the name implies, this type of disease develops mainly in people suffering from other skin or other diseases. Most often it is tuberculosis, malaria, leprosy, purulent skin lesions. Externally, the disease manifests itself in the form of the appearance on the skin of characteristic discs that are sufficiently dense to the touch, have a dark pink color, while the patient is experiencing severe itching.
Diagnosis of Amyloidosis of the Skin
Diagnosis of primary amyloidosis is difficult and requires the use of all possible methods. Secondary amyloidosis of organs is somewhat easier to recognize, since a disease is known that can lead to its development.
There are no specific laboratory changes in amyloidosis. However, the patients are characterized by the presence of significantly increased ESR (50-70 mm / h) and anemia (in some cases thrombocytosis, hyperfibrinogenemia). Special samples for amyloid are also used (with congoratum, methylene blue, which normally change urine color, whereas in patients they are fixed with amyloid and excreted with urine in minimal quantities), and electrophoretic examination of urine proteins.
At an amyloidosis of heart on an ECG low voltage of the QRS complex is registered. When conducting echocardiography, a combination of increased echogenicity (permeability) of the myocardium and thickening of the atrial walls is noted, which in 60-90% of cases indicates amyloidosis.
In the proteinuric stage of amyloidosis of the kidneys, an insignificant amount of protein in the urine and the periodic appearance of erythrocytes are detected, which is sometimes detected only in the study of urine sediment according to the Kakovsky Addis method. In addition, single cylinders (hyaline, granular, waxy) and white blood cells are determined in the urine. In some cases, renal blood flow and filtration are slightly reduced. In the nephrotic stage, the amount of albumin increases, globulins, especially their large particles, predominate among urine proteins. There is a high content of gamma glycoproteins and alpha lipoproteins in the urine. A small amount of erythrocytes, cylinders and often leukocytes are found in the urine sediment. There is a decrease in the level of blood proteins in violation of their ratio (albumin-globulin ratio decreases to 1.0 and below), alpha-2 and gamma fractions predominate among globulins. Elevated blood cholesterol levels may occur. Sometimes a moderate increase in creatinine, urea and residual nitrogen is detected in the blood. There may be slight changes in the fundus. Great importance in the diagnosis belongs to the kidney biopsy. In addition, the results of radiological and radio indication methods help to clarify the diagnosis.
In liver amyloidosis, a laboratory study reveals characteristic protein shifts, especially alpha-2-globulinemia, immune disorders, serum alkaline phosphatase activity is often increased, other functional tests are little changed. Puncture liver biopsy has the greatest diagnostic value.
Treatment of Amyloidosis of the Skin
Vitamin preparations are prescribed in large dosages, especially A. Inside, in the form of a solution, prescribe vitamins E, groups B, PP. In the area of lesions with a strong feeling of itching that disrupts sleep and the normal life of the patient, anesthetic solutions are injected. Various ointments are used, which are now widely represented in the pharmacological market. Forecast. Amyloidosis occurs chronically for a long time. In severe forms of the disease, the prognosis is poor. The best prognosis for recovery is with a lichenoid type of disease. However, for any outcome, you should always fear the possibility of developing the disease anew. Therefore, such patients should be under the supervision of a dermatologist for a long time.