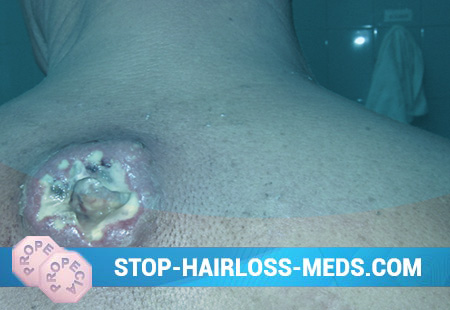
What is a Сarbuncle?
Carbuncle (lat. Carbunculus, literally “coal”; the old Russian name is fireworm, carbohydrate) is an acute purulent-necrotic inflammation of the skin and subcutaneous tissue around a group of hair sacs and sebaceous glands, which tends to spread rapidly.
Carbuncle is a diffuse purulent-necrotic inflammation of the deep layers of the dermis and hypodermis with the involvement of several neighboring hair follicles. With a carbuncle, a purulent-necrotic infiltrate occupies a large area and spreads in the deeper layers of the dermis and hypodermis than with a boil.
The word “carbuncle” comes from the Greek word carbo – coal and means “carbohydrate”, since large areas of necrosis formed during purulent-necrotic inflammation are dark in color, which served as the basis for the comparison of the disease with coal.
Favorite location – the back of the neck, back, lower back.
Causes of Carbuncle
The causative agent of the carbuncle is Staphylococcus aureus, less commonly, other types of staphylococcus.
Pathogenesis during Carbuncle
In the pathogenesis of the carbuncle, depletion (due to chronic malnutrition or a severe general illness) and metabolic disorders, especially carbohydrate (with diabetes mellitus) play a role.
Symptoms of Carbuncle
At the beginning of the development of the carbuncle, several separate dense nodules are found in the skin, which merge into one infiltrate. The latter increases, sometimes reaching the size of a child’s palm. Its surface takes on a hemispherical shape, the skin becomes tense, in the center of the infiltrate it is colored cyanotic: local pain is expressed. This is the first stage of the development of infiltrate, which lasts 8-12 days. Then, several pustules are formed in the infiltrate region, the tires of which are opened, and several holes are formed, giving the carbuncle a look that resembles a sieve. Through these holes, pus and necrotic masses of green color with an admixture of blood are secreted. Gradually, all large sections of the center of the carbuncle undergo necrosis. The rejected masses form an extensive tissue defect – a deep ulcer is formed, sometimes reaching the muscles. The second stage – the stage of suppuration and necrosis – lasts from 14 to 20 days. Further, the ulcer is filled with granulation tissue and, as a rule, a coarse deep scar welded with the underlying tissues is formed. Large scars remain after surgery if it is carried out for carbuncle.
Usually there are single carbuncles. Their development is accompanied by high fever, excruciating pains of a tearing, tugging character, chills, malaise. The malignant course of the carbuncle can be observed in old age, in malnourished patients suffering from severe diabetes, with neuropsychic overwork. In these cases, neuralgic pains, delirium or deep prostration, septic fever appear. Death can occur from profuse bleeding from a large vessel and from sepsis. With localization in the nose, upper lip, severe meningeal complications are possible.
Carbuncle Diagnosis
The diagnosis is not difficult. It should be remembered about anthrax carbuncle, in which tissue edema is more pronounced; in the area of the pustule, the formation of a black scab resembling coal (anthrax) is observed, and a specific pathogen is detected – aerobic gram-positive anthrax bacillus. It is easy to distinguish carbuncle from a boil on the basis of the clinical picture described above.
Carbuncle Treatment
On an outpatient basis, treatment of small carbuncles that are localized on the trunk and limbs, in the absence of severe intoxication, is acceptable. At the beginning of the disease, in the presence of only inflammatory infiltrate, before the formation of a purulent-necrotic focus, antibiotic therapy is indicated. Prescribe antibiotics, as a rule, with a wide spectrum of action – ampicillin, ampiox, etc., synthetic antibacterial drugs with a wide spectrum of action – biseptol, furagin. Analgesic and cardiac agents, a dairy and vegetable diet are indicated. The surface of the infiltrate is treated with 70% ethyl alcohol and an aseptic dressing is applied. Apply ultraviolet radiation, UHF therapy. With the favorable effect of conservative therapy, the reverse development of infiltrate occurs after 2 to 3 days and is accompanied by a decrease in pain, a decrease in body temperature, and normalization of the blood picture.
An indication for carbuncle surgery is the formation of a focus of necrosis. An operation for a small carbuncle is performed under local anesthesia with a 0.5 – 0.25% solution of novocaine. The carbuncle is crosswise dissected through the entire thickness of necrosis to viable tissues, followed by necrectomy. The operation is completed by the introduction of tampons with a hypertonic solution of sodium chloride or proteolytic enzymes into the wound. Before the final rejection of purulent-necrotic masses, dressings with proteolytic enzymes, a hypertonic sodium chloride solution are replaced daily, stage-wise necrectomies are performed, then ointment-based preparations are used (10% methyluracil ointment, vinylin, etc.). After the operation, antibiotic therapy and physiotherapy are continued.
The large size of the carbuncle, the progression of the purulent-necrotic process, uncompensated diabetes mellitus, the increase in intoxication are an indication for hospitalization. Treatment of a carbuncle localized on the face must also be carried out in a hospital.
Carbuncle Prevention
Prevention of carbuncle is the hygienic content of skin and linen.